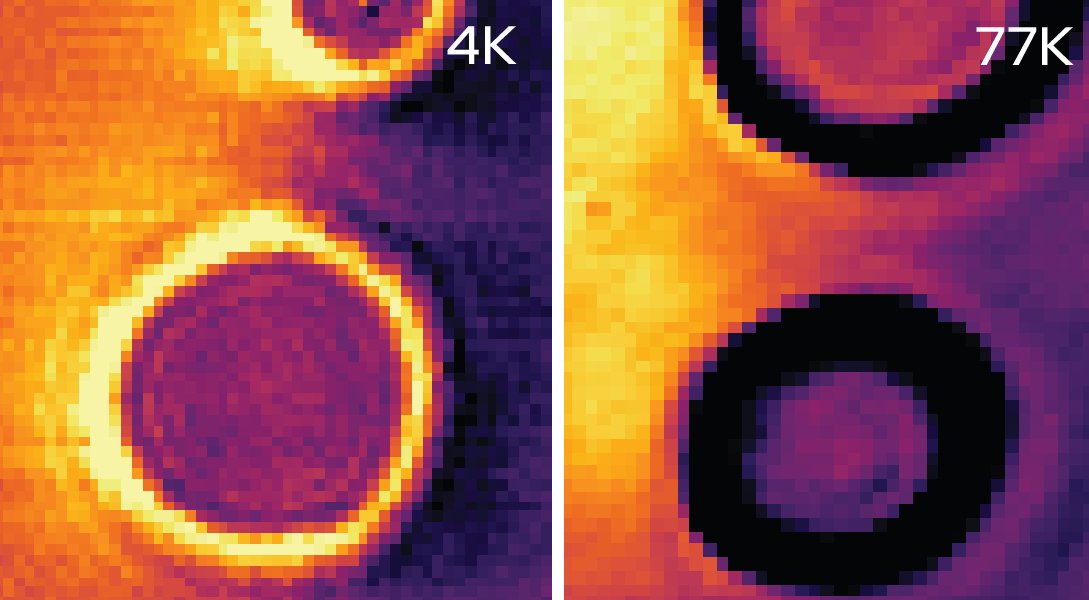
Physicists at the University of Wisconsin–Madison directly measured, for the first time at nanometer resolution, the fluid-like flow of electrons in graphene. The results, which will appear in the journal Science on Feb. 17, have applications in developing new, low-resistance materials, where electrical transport would be more efficient.
Graphene, an atom-thick sheet of carbon arranged in a honeycomb pattern, is an especially pure electrical conductor, making it an ideal material to study electron flow with very low resistance. Here, researchers intentionally added impurities at known distances and found that electron flow changes from gas-like to fluid-like as temperatures rise.
“All conductive materials contain impurities and imperfections that block electron flow, which causes resistance. Historically, people have taken a low-resolution approach to identifying where resistance comes from,” says Zach Krebs, a physics graduate student at UW–Madison and co-lead author of the study. “In this study, we image how charge flows around an impurity and actually see how that impurity blocks current and causes resistance, which is something that hasn’t been done before to distinguish gas-like and fluid-like electron flow.”
Read the full story


